Agriculture has been the backbone of India’s economy for centuries, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing to the nation’s food security. However, traditional farming methods face challenges such as climate variability, water scarcity, declining soil fertility, and inefficient supply chains. To address these issues and enhance productivity, Indian agriculture is increasingly adopting modern technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies promise to transform the sector by making farming more efficient, sustainable, and data-driven. This article explores the role of AI and IoT in Indian agriculture, their applications, benefits, challenges, and future potential.
AI and IoT are revolutionizing agriculture by enabling precision farming, real-time monitoring, predictive analysis, and automation. Precision agriculture involves applying the right amount of inputs, such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, at the right time and place, minimizing waste and increasing yields. IoT devices, including sensors, drones, and smart irrigation systems, collect data on soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. AI algorithms then analyze this data to provide actionable insights for farmers, helping them make informed decisions.
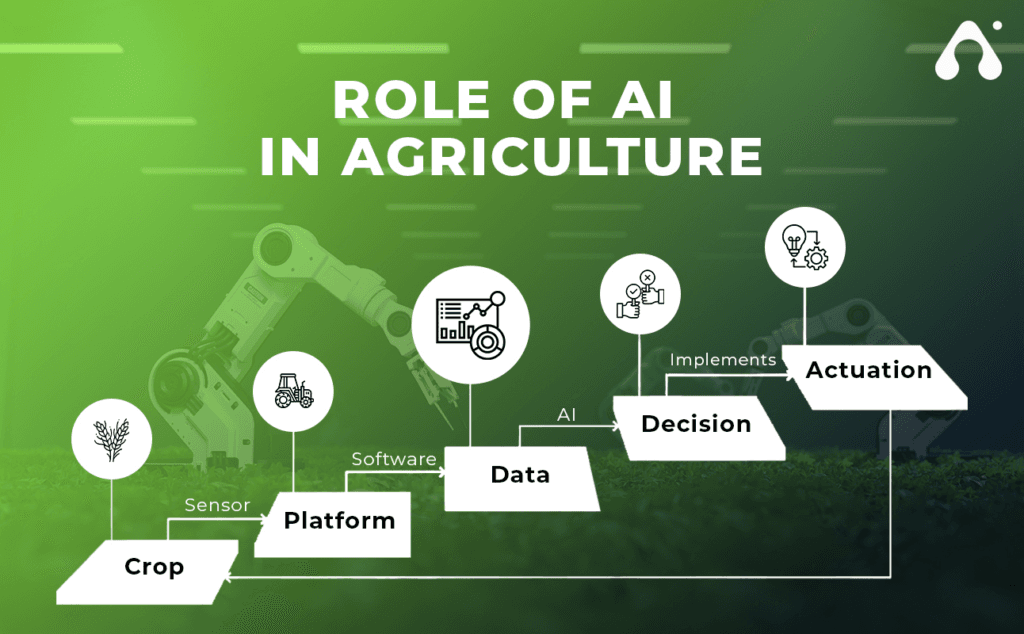
Applications of AI in Agriculture
Artificial Intelligence has multiple applications in modern agriculture, enhancing decision-making, risk management, and operational efficiency. AI-powered tools can analyze satellite imagery, weather forecasts, and historical crop data to predict yields, detect diseases, and optimize planting schedules. Machine learning models help identify patterns that are not easily visible to the human eye, enabling early interventions and reducing crop losses.
AI is also being used in pest and disease management. Image recognition technology can detect signs of infestation or infection in crops, allowing farmers to take timely action. Additionally, AI-driven robots and machinery can perform repetitive tasks like sowing, weeding, and harvesting, reducing labor dependency and improving productivity. AI applications are increasingly integrated with mobile platforms, allowing farmers to access recommendations, alerts, and market trends remotely, even from rural areas with limited connectivity.
IoT in Indian Agriculture
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables connectivity between physical devices, sensors, and data platforms, providing real-time insights into agricultural processes. IoT sensors can monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, temperature, humidity, and crop growth, sending data to centralized systems for analysis. Smart irrigation systems use this information to optimize water usage, reducing wastage and conserving resources.
IoT also supports supply chain efficiency by tracking storage conditions, transportation, and distribution of agricultural produce. Cold chain monitoring, for example, ensures that perishable goods reach markets without spoilage, reducing post-harvest losses. Drones equipped with IoT sensors are used for aerial surveillance, mapping fields, and spraying fertilizers or pesticides more accurately. These technologies collectively enhance productivity, sustainability, and profitability for farmers.
Benefits of AI and IoT Integration
The integration of AI and IoT in agriculture offers several advantages that can transform Indian farming:
- Increased Productivity: Precision farming and data-driven insights enable optimal use of resources, resulting in higher crop yields and improved quality.
- Resource Efficiency: Smart irrigation, automated machinery, and AI-driven input recommendations reduce water, fertilizer, and energy usage, lowering costs and environmental impact.
- Early Disease and Pest Detection: AI and IoT systems can detect anomalies in crop health, preventing large-scale losses and minimizing pesticide use.
- Better Market Access: Digital platforms provide farmers with real-time market information, helping them make informed pricing and selling decisions.
- Sustainability: Efficient use of resources, reduced chemical inputs, and soil monitoring contribute to environmentally sustainable farming practices.
By adopting AI and IoT, Indian farmers can transition from traditional, intuition-based farming to modern, data-driven agriculture that supports economic growth, environmental sustainability, and food security.

Challenges in Adoption
Despite the clear benefits, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of AI and IoT in Indian agriculture. First, high initial costs of devices, sensors, drones, and AI platforms can be prohibitive for small-scale farmers. Access to affordable financing, subsidies, and government support is critical to overcoming this barrier.
Second, digital literacy remains a challenge in rural areas. Many farmers are not familiar with advanced technologies or how to interpret data insights. Training programs, farmer education initiatives, and user-friendly platforms are necessary to ensure effective utilization.
Third, connectivity and infrastructure limitations, such as inconsistent internet coverage and electricity shortages, can affect the deployment of IoT devices and cloud-based AI systems. Solutions like low-power IoT devices, offline analytics, and community-level support centers can help bridge these gaps.
Data privacy and security are additional concerns. AI and IoT platforms collect vast amounts of sensitive agricultural and personal data. Ensuring proper data protection, secure storage, and responsible usage is essential to maintain trust among farmers and stakeholders.
Government Initiatives and Industry Collaboration
The Indian government has recognized the potential of AI and IoT in agriculture and launched several initiatives to promote their adoption. Programs under the Digital India and Smart Agriculture missions aim to provide technological support, farmer training, and funding for innovation. Subsidies and incentives for IoT devices, precision farming equipment, and AI platforms are gradually becoming available.
Private sector collaborations are also playing a key role. Startups, agri-tech companies, and technology providers are developing AI and IoT solutions tailored to Indian conditions. Companies are offering subscription-based models, shared infrastructure, and advisory services to make advanced technologies accessible to smallholder farmers. Collaborative efforts between research institutions, government agencies, and private enterprises are accelerating innovation and deployment at scale.
Future Outlook
The future of Indian agriculture is poised for transformation through AI and IoT. As technology adoption increases, farmers will gain access to real-time insights, predictive analytics, and automated farming solutions that improve efficiency and profitability. Integration with emerging technologies such as blockchain can enhance traceability, supply chain transparency, and farm-to-fork accountability.
Smart farming solutions will also support climate resilience by providing early warnings for droughts, floods, and extreme weather events. Adoption of AI and IoT can reduce resource wastage, improve sustainability, and boost India’s competitiveness in the global agricultural market. Over the next decade, the combination of technology-driven farming, government support, and industry collaboration is likely to make Indian agriculture more modern, resilient, and profitable.

Conclusion / Final Thoughts
In conclusion, AI and IoT are transforming Indian agriculture by enabling precision farming, resource efficiency, and data-driven decision-making. These technologies enhance productivity, sustainability, and profitability while addressing challenges such as climate variability, labor shortages, and supply chain inefficiencies. Despite barriers related to cost, connectivity, and digital literacy, government initiatives, private sector innovations, and collaborative approaches are fostering adoption across the country. As AI and IoT continue to evolve, Indian agriculture is likely to emerge as a more resilient, efficient, and technologically advanced sector, contributing to food security, economic growth, and sustainable development.
FAQs
1. How does AI help farmers in India?
AI analyzes data from weather, soil, and crop health to provide actionable insights for planting, irrigation, pest management, and yield prediction.
2. What is the role of IoT in agriculture?
IoT devices collect real-time data on soil, water, climate, and crop conditions, enabling smart irrigation, monitoring, and automation to increase efficiency.
3. What challenges do Indian farmers face in adopting AI and IoT?
High initial costs, limited digital literacy, poor connectivity, and data security concerns are key challenges to adoption.
4. Are government initiatives supporting AI and IoT in agriculture?
Yes, programs under Digital India, Smart Agriculture, and other subsidy schemes aim to promote technology adoption and provide training for farmers.
Next Topic: Smart Cities Mission in India: Progress and Challenges
Also Check: Silver Investment in India: Price Trends & Future Outlook
