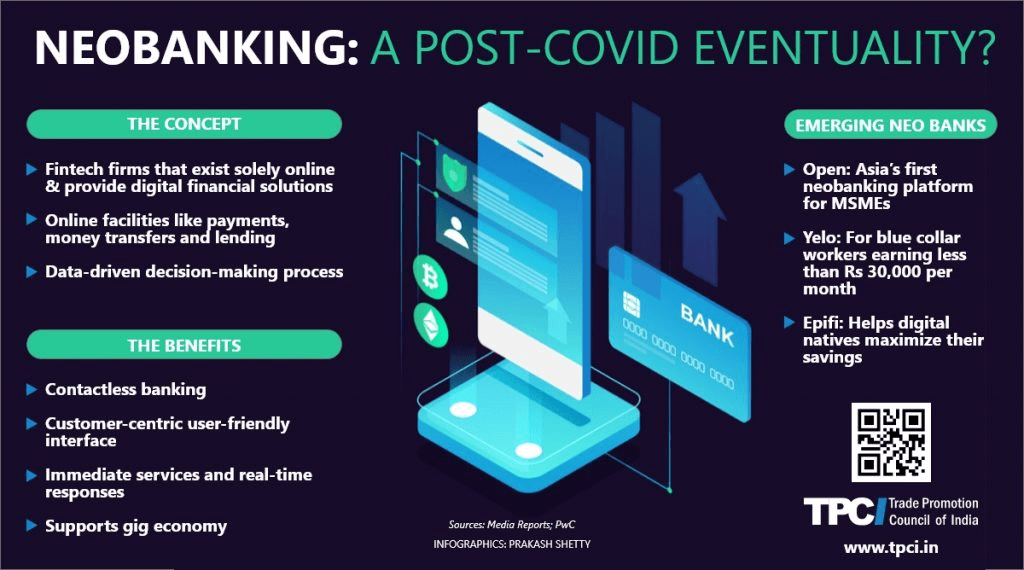
Neobanks have emerged as a disruptive force in India’s financial ecosystem, offering digital-first banking solutions that cater to the needs of tech-savvy consumers and small businesses. Unlike traditional banks, neobanks operate without physical branches and rely heavily on mobile applications and cloud-based infrastructure. This allows them to provide faster, more convenient, and often more cost-effective financial services. With increasing smartphone penetration, digital literacy, and a growing preference for cashless transactions, neobanks are steadily gaining popularity in India. This article explores the rise of neobanks, their features, regulatory framework, benefits, challenges, and their potential to transform the future of banking in India.
Neobanks are designed to simplify banking, offering services such as digital savings accounts, payment solutions, expense management, and lending facilities. They leverage advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, data analytics, and automation to deliver personalized experiences. Startups such as RazorpayX, Niyo, Open, and Jupiter are leading the neobank revolution in India, targeting both retail customers and SMEs who often face hurdles with conventional banking processes.

The Rise of Neobanks in India
The growth of neobanks in India has been fueled by several factors. First, the rapid adoption of smartphones and mobile internet has created a large digitally connected population that prefers online solutions over physical banking. Second, the pandemic accelerated the shift toward contactless payments and digital financial services, prompting users to seek convenient alternatives to traditional banking. Third, government initiatives such as the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Digital India, and financial inclusion programs have created a robust digital payments infrastructure that neobanks can leverage to expand their services.
Neobanks often partner with traditional banks to provide regulated banking services, since they do not hold a banking license themselves. This partnership allows neobanks to offer savings accounts, debit cards, and other banking products while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. The combination of technology-driven solutions and bank partnerships enables neobanks to streamline onboarding, reduce paperwork, and enhance customer experience compared to conventional banking channels.
Key Features and Offerings
Neobanks distinguish themselves from traditional banks through several key features. First, they offer a seamless digital experience, allowing users to open accounts, make payments, track expenses, and manage finances entirely through mobile applications. Second, neobanks often provide value-added services such as automated budgeting, expense categorization, bill reminders, and credit score tracking. Third, they cater to niche segments, including freelancers, gig economy workers, and small businesses, offering specialized solutions such as invoicing, payroll management, and instant business loans.
Another defining feature of neobanks is cost-effectiveness. By eliminating physical infrastructure, these platforms reduce operational costs and often pass the savings on to customers through lower fees, zero minimum balance requirements, and attractive rewards. Many neobanks also integrate with other financial services, such as investment platforms, insurance providers, and lending solutions, creating a one-stop ecosystem for financial management.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Although neobanks are not licensed as full-fledged banks, they operate within India’s regulatory framework by partnering with RBI-regulated banks. These partner banks hold customer deposits and ensure compliance with statutory requirements, including KYC, anti-money laundering (AML), and data security regulations. Neobanks themselves must adhere to guidelines regarding data protection, secure transactions, and consumer rights, ensuring that customers benefit from the safety and reliability of regulated banking while enjoying digital convenience.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other regulatory authorities have been supportive of digital banking innovations while emphasizing prudential norms. Neobanks must ensure transparency in pricing, interest rates, and product terms. Additionally, the emergence of neobanks has prompted discussions on data privacy, cybersecurity, and regulatory oversight to safeguard consumer interests in the evolving digital finance landscape.
Benefits for Consumers and Businesses
Neobanks offer several advantages over traditional banks for both retail and business customers. For individuals, they provide quick account opening, intuitive apps for financial management, instant notifications for transactions, and easy access to savings and investment options. Many neobanks offer rewards, cashback, or zero fees on transfers, enhancing the overall customer experience.
For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), neobanks address pain points associated with traditional banking, such as delayed loan approvals, complex documentation, and cumbersome payroll management. By offering integrated financial solutions, instant payments, and digital invoicing tools, neobanks improve cash flow management and operational efficiency. The flexibility and transparency provided by neobanks enable businesses to make better financial decisions and scale operations more effectively.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, neobanks face challenges that could impact their adoption and growth. Regulatory uncertainty remains a key concern, as authorities continue to evaluate how digital banking solutions fit within India’s broader financial ecosystem. Consumer trust is another factor, as users may be hesitant to entrust funds to a digital-only platform without a physical presence.
Profitability is also a challenge for neobanks, as low fees and free services may limit revenue generation in the short term. Customer acquisition and retention require continuous innovation, marketing, and superior service quality. Additionally, cybersecurity risks and data breaches pose threats that neobanks must mitigate through robust technology and compliance measures.
The Future of Banking in India
Neobanks are likely to play a transformative role in India’s banking sector, complementing rather than replacing traditional banks. By focusing on convenience, personalization, and efficiency, neobanks are reshaping customer expectations and driving innovation. Traditional banks are responding by enhancing their digital offerings, forming partnerships with fintech companies, and adopting technology-driven solutions to remain competitive.
The future of banking in India may involve a hybrid ecosystem where neobanks and traditional banks coexist, offering specialized services tailored to different customer segments. The integration of AI, machine learning, and data analytics will enable personalized financial products, better risk management, and improved customer engagement. As digital literacy continues to grow, neobanks have the potential to expand financial inclusion and empower a new generation of consumers and businesses to manage their finances more effectively.

Conclusion / Final Thoughts
In conclusion, neobanks in India represent a significant shift in the way financial services are delivered and consumed. By leveraging technology, mobile connectivity, and partnerships with traditional banks, they offer innovative, user-friendly, and cost-effective solutions for individuals and businesses. While challenges such as regulatory compliance, cybersecurity, and profitability exist, the overall outlook remains positive. Neobanks are likely to complement conventional banking, driving digital adoption, financial inclusion, and operational efficiency. As India’s economy continues to evolve and consumers increasingly demand convenience and transparency, neobanks are poised to play a key role in shaping the future of banking in the country.
FAQs
1. What is a neobank, and how is it different from traditional banks?
A neobank is a digital-only bank that operates primarily through mobile apps and online platforms, offering banking services without physical branches. It differs from traditional banks in terms of convenience, technology integration, and often lower fees.
2. Are neobanks in India safe to use?
Yes, most neobanks operate in partnership with RBI-regulated banks and adhere to KYC, AML, and data security guidelines to ensure user funds and data are protected.
3. What services do neobanks offer for businesses?
Neobanks provide services like digital accounts, instant payments, invoicing, payroll management, and business loans, helping SMEs manage finances efficiently.
4. Can neobanks replace traditional banks in India?
While they complement traditional banks by offering innovative digital solutions, neobanks are unlikely to fully replace them. A hybrid ecosystem combining both is expected to shape India’s banking future.
Next Topic: Silver Investment in India: Price Trends & Future Outlook
Also Check: T20 World Cup 2026 Ticket Sales Go Live: Fans Rush to Secure Spots for Cricket’s Grandest Stage
