Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) has become a critical component of India’s energy strategy, offering a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional fossil fuels like coal and oil. Over the past decade, India’s LNG imports and domestic consumption have increased steadily, driven by rising industrial demand, power generation needs, and government policies promoting cleaner energy. As India seeks to balance energy security, sustainability, and economic growth, understanding the trends, drivers, challenges, and future prospects of LNG demand is essential for policymakers, investors, and industry stakeholders. This article provides a comprehensive overview of India’s LNG market, its growth trajectory, key drivers, business opportunities, and outlook for the coming decade.
LNG is natural gas cooled to -162°C, which reduces its volume by approximately 600 times, making it easier and more cost-effective to transport over long distances where pipelines are not feasible. Once regasified, LNG can be used in electricity generation, industrial processes, domestic cooking, and transportation. India’s strategic focus on LNG aligns with its commitments to reduce carbon emissions, increase energy efficiency, and diversify energy imports. With global energy markets evolving rapidly, LNG offers India the flexibility to meet growing energy needs while transitioning toward cleaner fuels.

Current State of LNG Demand in India
India is the world’s fourth-largest LNG importer, with imports primarily concentrated at terminals in Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh. Major ports handling LNG include Dahej, Hazira, Kochi, Ennore, and Mundra. Annual LNG imports have increased steadily, reaching around 32 million tonnes in 2022, with the majority sourced from countries such as Qatar, the United States, Russia, and Australia.
LNG consumption in India spans multiple sectors:
- Power Generation:
Gas-based power plants contribute to a cleaner energy mix, supplementing coal-fired generation. Natural gas allows for flexible generation and lower carbon emissions, supporting India’s climate commitments. - Industrial Use:
Industries such as fertilizers, chemicals, steel, and cement increasingly rely on LNG for its energy efficiency and cost advantages. The consistent supply of LNG supports high-energy industrial operations. - City Gas Distribution (CGD):
LNG is supplied through pipelines and CNG stations for domestic and commercial use in urban areas. Expansion of CGD networks in cities improves energy access and reduces dependence on polluting fuels like kerosene and LPG. - Transportation:
The push for cleaner fuels in transportation, including trucks, buses, and shipping, has led to growing adoption of LNG and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG), reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency.

Drivers of LNG Demand Growth
Several factors are driving the increasing demand for LNG in India:
- Energy Security and Diversification:
India relies heavily on energy imports, particularly crude oil and coal. LNG provides a diversified source of energy, helping reduce dependence on a single fuel type and enhancing energy security. - Environmental Regulations:
Government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality encourage the adoption of cleaner fuels. LNG, with its lower carbon intensity compared to coal and oil, aligns with India’s environmental goals. - Government Policy and Incentives:
Initiatives such as the National Gas Grid, expansion of city gas distribution networks, and tax incentives for gas-based industries have created a favorable environment for LNG growth. The government’s vision to increase the share of natural gas in India’s energy mix from 6% to 15% by 2030 further drives investment and demand. - Infrastructure Development:
New LNG terminals, regasification facilities, pipelines, and storage capacities are being developed to meet rising demand. Investments in import terminals and distribution infrastructure improve accessibility and reduce logistical bottlenecks. - Industrial and Urban Demand:
Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and economic growth increase demand for reliable energy. LNG’s flexibility in industrial processes and urban energy applications makes it a preferred choice. - Global Market Dynamics:
Favorable long-term contracts, competitive global LNG pricing, and improved logistics facilitate India’s ability to secure supply from multiple international sources. Strategic partnerships with LNG exporting nations ensure stable and diversified supply.
Business Opportunities in India’s LNG Sector
The growth of LNG demand presents several business opportunities across the supply chain:
- LNG Import and Terminal Operations:
Companies can invest in building and operating LNG import terminals, regasification units, and storage facilities. These assets are critical for ensuring reliable supply to industrial, urban, and power sectors. - City Gas Distribution (CGD):
Expanding urban gas networks offers opportunities for private companies to supply LNG and CNG to residential, commercial, and transportation sectors. Partnerships with local governments and industrial clusters can accelerate market penetration. - Transportation and Logistics:
LNG logistics, including cryogenic storage tanks, transportation vessels, and trucking services, create opportunities for specialized service providers. Efficient logistics are essential for maintaining supply chain integrity and reducing costs. - Industrial and Power Projects:
Setting up gas-fired power plants, fertilizer plants, and energy-intensive industries reliant on LNG creates direct business opportunities. Companies adopting LNG-based technologies benefit from lower energy costs and compliance with environmental regulations. - Renewable Integration and Hybrid Solutions:
Opportunities exist in integrating LNG with renewable energy systems for hybrid power generation. Gas-based plants complement intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind, providing stable and efficient energy. - Trading and Investment:
LNG trading, long-term supply agreements, and investment in global LNG projects offer opportunities for Indian companies and investors to secure supply and hedge against price volatility.
Challenges in the LNG Market
Despite strong growth prospects, India’s LNG sector faces several challenges:
- Price Volatility:
Global LNG prices are influenced by demand-supply dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and shipping costs. Price fluctuations can affect the cost competitiveness of LNG compared to domestic fuels. - Infrastructure Gaps:
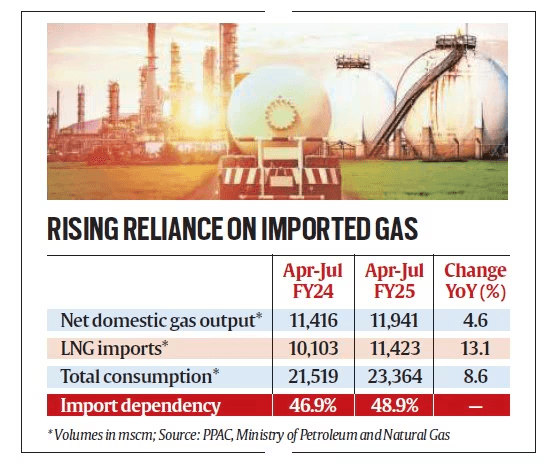
While major ports have LNG terminals, limited pipeline connectivity in some regions restricts access. Expanding the natural gas grid and developing regional distribution networks are essential. - Import Dependency:
India imports the majority of its LNG, exposing the country to global supply disruptions and exchange rate risks. Diversifying suppliers and exploring domestic production, including liquefied natural gas from domestic gas fields, is crucial. - Regulatory and Policy Uncertainty:
Policy changes, pricing regulations, and tariffs can impact investment decisions. A stable regulatory environment is necessary to attract private sector investment. - Environmental and Social Considerations:
Developing LNG infrastructure requires careful environmental assessment and community engagement. Storage terminals, pipelines, and transport systems must adhere to safety and environmental standards.
Future Outlook
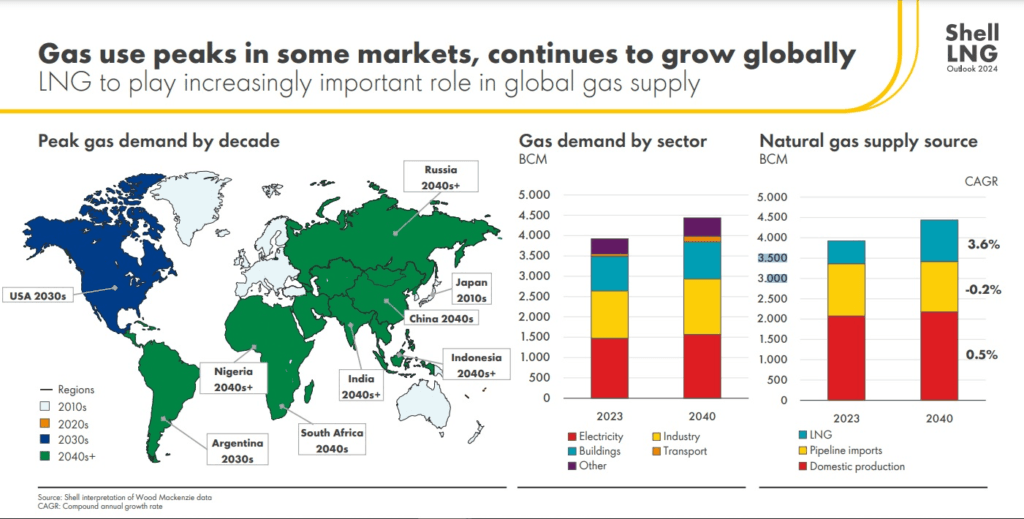
India’s LNG demand is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6-8% over the next decade, driven by industrial expansion, power generation, and the expansion of city gas networks. Key trends shaping the future include:
- Expansion of LNG Terminals:
Several new terminals are under construction, increasing import capacity and reducing bottlenecks in supply. Strategic locations along the western and eastern coasts will improve accessibility. - Integration with Renewable Energy:
Gas-fired plants will increasingly complement solar and wind energy, providing flexible and reliable power solutions. Hybrid energy solutions are likely to gain traction in industrial and urban settings. - Increased Use in Transportation:
Adoption of LNG in trucking, shipping, and commercial transport is expected to rise as governments and companies seek cleaner alternatives to diesel and fuel oil. - Domestic Production and Supply Diversification:
Exploration of domestic gas reserves, LNG liquefaction projects, and international long-term contracts will help secure supply and reduce dependence on a limited number of exporters. - Investment Opportunities:
Private sector participation, foreign direct investment, and public-private partnerships will drive infrastructure development, technology adoption, and efficient distribution networks.
Conclusion / Final Thoughts
LNG has emerged as a vital component of India’s energy transition, offering a cleaner, efficient, and flexible fuel for industrial, power, and urban applications. Rising domestic demand, government support, expanding infrastructure, and global supply opportunities make India an attractive market for LNG investments. While challenges like price volatility, infrastructure gaps, and import dependency exist, strategic planning, technology adoption, and policy support can mitigate risks. The growth of LNG aligns with India’s goals of energy security, economic development, and environmental sustainability. As demand continues to rise, LNG will play a pivotal role in powering India’s industries, cities, and transportation networks, creating new business opportunities and strengthening the country’s energy ecosystem.
FAQs
1. Why is LNG demand growing in India?
Demand is rising due to industrial expansion, cleaner energy requirements, power generation needs, city gas distribution growth, and supportive government policies.
2. Which sectors consume the most LNG in India?
Major sectors include power generation, industrial manufacturing (fertilizers, chemicals, steel), city gas distribution, and transportation.
3. What are the key business opportunities in India’s LNG sector?
Opportunities exist in LNG import terminals, city gas distribution, industrial projects, logistics, trading, and hybrid energy solutions.
4. What challenges does India face in LNG supply and consumption?
Challenges include global price volatility, limited pipeline infrastructure, import dependency, regulatory uncertainty, and environmental considerations.
Next Topic: Australia Tour of Pakistan 2026: A High-Stakes Final Countdown to the T20 World Cup
Also Check: PLI Schemes Explained: Benefits for Indian Manufacturers
