The financial services landscape in India is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the rapid growth of fintech startups and digital financial solutions. Traditional banking models are being challenged by innovative technologies, customer-centric platforms, and new business models that focus on accessibility, efficiency, and convenience. By 2026, fintech disruption in India has reshaped the way individuals, businesses, and institutions interact with financial services, offering unprecedented opportunities and challenges for banks, regulators, and investors alike.
Rise of Fintech in India
India has emerged as a global hub for fintech innovation, fueled by favorable government policies, technological advancement, and rising smartphone penetration. Initiatives such as Digital India, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), and Jan Dhan Yojana have laid the groundwork for digital financial inclusion, enabling millions of previously unbanked individuals to access financial services.
The fintech ecosystem in India spans multiple sectors, including digital payments, lending, insurance technology (InsurTech), wealth management, and regulatory technology (RegTech). Startups in these areas leverage artificial intelligence, blockchain, big data analytics, and mobile technology to provide seamless, secure, and efficient financial solutions.
Digital Payments and Banking Transformation
Digital payments have been a key driver of fintech disruption in India. Platforms such as Paytm, PhonePe, and Google Pay have revolutionized peer-to-peer payments, e-commerce transactions, and bill payments. The adoption of UPI has made instant, real-time payments ubiquitous, reducing dependency on cash and traditional banking infrastructure.
Banks are responding to this shift by partnering with fintech companies, integrating digital wallets, and upgrading mobile banking platforms. Neo-banks and digital-only banks have also emerged, offering low-cost, fully digital banking services without the need for physical branches. This transformation is enhancing customer experience while reducing operational costs for financial institutions.
Fintech Lending and Credit Solutions
Traditional lending in India has often been constrained by lengthy processes, limited credit history data, and geographical barriers. Fintech lending platforms are addressing these challenges by using alternative data, machine learning algorithms, and digital verification processes to provide instant loans, microcredit, and peer-to-peer lending solutions.
Startups such as Razorpay, Lendingkart, and Indifi are enabling small businesses and entrepreneurs to access credit with minimal documentation and faster disbursal. By leveraging technology, fintech lenders are expanding financial inclusion and fostering entrepreneurship across urban and rural India.
InsurTech and Wealth Management Innovations
Insurance technology (InsurTech) is another area where fintech disruption is reshaping the Indian market. Startups offer digital insurance products, automated claims processing, and personalized policies that cater to diverse customer needs. Platforms like PolicyBazaar simplify insurance comparison and purchase, while AI-driven analytics help insurers assess risk and detect fraud efficiently.
In wealth management, fintech platforms provide automated investment solutions, robo-advisors, and personalized portfolio management. Services like Groww, Zerodha, and ET Money empower individuals to invest in mutual funds, stocks, and digital assets with minimal fees, democratizing access to sophisticated financial planning tools.
Impact on Traditional Banks
The rise of fintech has forced traditional banks in India to rethink their strategies. Banks are now adopting digital-first approaches, partnering with fintech startups, and implementing API-driven solutions to remain competitive. Key impacts include:
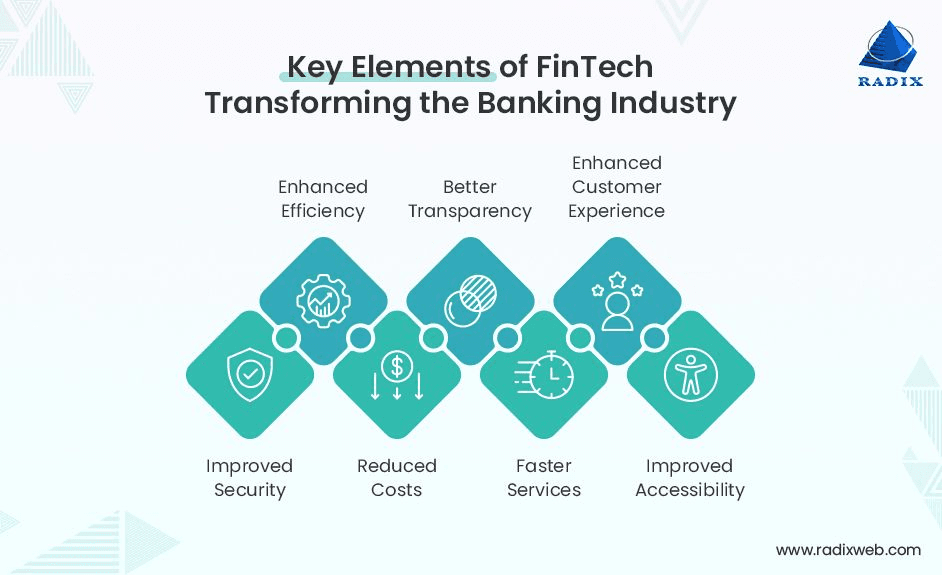
1. Enhanced Customer Experience: Banks are offering mobile apps, AI chatbots, and real-time notifications to improve user engagement and service quality.
2. Operational Efficiency: Digital solutions reduce paperwork, manual processes, and branch dependency, lowering operational costs.
3. Financial Inclusion: Collaborations with fintech companies extend banking services to underserved populations, particularly in rural areas.
4. Competitive Pressure: Traditional banks face competition from neo-banks and fintech platforms that offer faster, cheaper, and more accessible financial services.
Regulatory and Security Considerations
With fintech growth, regulators such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) have implemented frameworks to ensure consumer protection, data privacy, and systemic stability. Guidelines on digital lending, payments, and cybersecurity help mitigate risks while fostering innovation.
Security remains a key concern, as cyberattacks and fraud can threaten the integrity of digital financial platforms. Fintech companies are investing heavily in encryption, multi-factor authentication, and AI-driven fraud detection to protect customer data and maintain trust.
Future Trends in Fintech
By 2026, several trends are shaping the future of fintech in India:
1. Embedded Finance: Fintech solutions will increasingly integrate into non-financial platforms such as e-commerce, mobility, and social apps, offering seamless financial services within everyday activities.
2. Blockchain and Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain technology will enable secure, transparent transactions, while DeFi platforms may create alternative financial ecosystems for lending, payments, and investments.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics: AI will enhance personalization, fraud detection, and decision-making for both consumers and financial institutions.
4. Expansion into Tier 2 and Tier 3 Cities: Fintech penetration in smaller cities and rural areas will drive financial inclusion, leveraging mobile platforms and local agents.
5. Sustainable and Ethical Finance: Fintech platforms will increasingly focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) principles, offering green loans, impact investing, and socially responsible financial products.
Conclusion
Fintech disruption in India is redefining the financial services landscape, challenging traditional banks while expanding access, efficiency, and innovation. Digital payments, lending platforms, InsurTech, and wealth management solutions have transformed the way individuals and businesses engage with finance.
Traditional banks, regulators, and fintech startups must collaborate to ensure secure, inclusive, and sustainable growth. As technology adoption continues to rise, fintech in India promises to enhance financial inclusion, promote entrepreneurship, and contribute to the overall economic development of the country. Investors, entrepreneurs, and policymakers should closely monitor this evolving sector to leverage opportunities and address emerging challenges effectively.
FAQs
1. What is fintech and how is it impacting India?
Fintech refers to technology-driven financial services. It impacts India by improving accessibility, efficiency, and customer experience in banking, payments, lending, insurance, and investments.
2. Which are some leading fintech startups in India?
Paytm, PhonePe, Razorpay, PolicyBazaar, Groww, and Zerodha are notable fintech companies driving innovation across various financial services.
3. How are traditional banks responding to fintech disruption?
Banks are adopting digital-first strategies, partnering with fintechs, integrating AI and mobile platforms, and focusing on customer experience and operational efficiency.
4. What are the future trends in India’s fintech sector?
Key trends include embedded finance, blockchain and DeFi solutions, AI-driven personalization, expansion into smaller cities, and sustainable financial products.
Next Topic: Healthcare Startups India 2026 – Growth & Opportunities
Also Check: India Infrastructure Growth 2026 – Roads, Railways & Ports
