India’s fintech sector has emerged as one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving segments of the economy, transforming the way individuals and businesses access financial services. With a large digitally-savvy population, rising smartphone penetration, and supportive government policies, fintech startups have created innovative business models that address gaps in banking, payments, lending, wealth management, and insurance. This article explores the key business models of Indian fintech startups and their impact on the financial ecosystem.

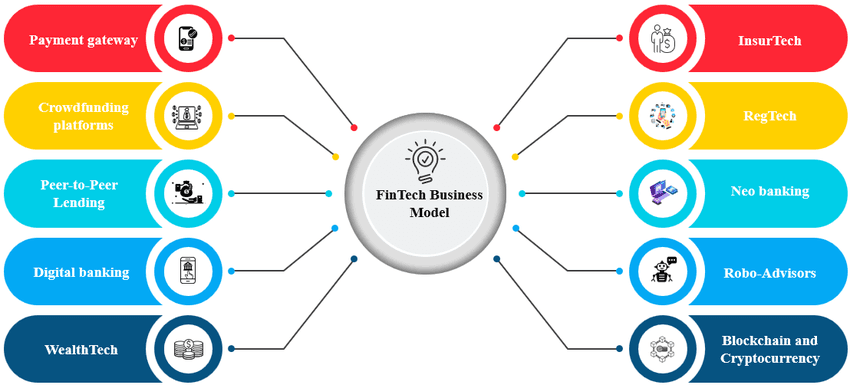
Digital Payments and Wallets
One of the most successful fintech business models in India revolves around digital payments and wallets. Companies like Paytm, PhonePe, Google Pay, and MobiKwik have developed platforms that allow users to transfer money, pay bills, recharge mobile phones, and shop online seamlessly.
These platforms often rely on a freemium model, offering basic services for free while monetizing through transaction fees, merchant commissions, and value-added services. Partnerships with banks, merchants, and payment networks enable startups to scale rapidly while maintaining low operational costs.
The introduction of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) further revolutionized digital payments, providing a secure and interoperable system for instant bank-to-bank transfers. Fintech startups leverage UPI to offer user-friendly apps with additional features like expense tracking, QR code payments, and loyalty programs, increasing adoption among both urban and rural users.
Lending Platforms and Credit Services
Fintech startups have also disrupted traditional lending by providing faster, more accessible, and technology-driven credit solutions. Companies like Lendingkart, Capital Float, and Indifi offer working capital loans, business loans, and personal loans using digital platforms and alternative credit scoring models.
These startups often adopt a peer-to-peer (P2P) or marketplace lending model, connecting borrowers with lenders while using data analytics and machine learning to assess creditworthiness. By minimizing paperwork, automating approvals, and leveraging technology, they provide faster disbursal of funds compared to traditional banks.
Micro-lending and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services have gained significant traction among consumers and small businesses. BNPL platforms like ZestMoney and Simpl enable instant credit for online and offline purchases, generating revenue through merchant fees and interest on deferred payments.
Wealth Management and Investment Platforms
Indian fintech startups have developed innovative business models in wealth management, targeting retail investors and millennials who are increasingly seeking digital solutions for investments. Companies like Groww, Zerodha, Upstox, and Paytm Money offer platforms for mutual funds, stock trading, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and systematic investment plans (SIPs).
These platforms often use a commission-free or low-cost model, earning revenue through premium features, advisory services, margin trading, or subscription plans. Technology-driven research tools, portfolio tracking, and personalized recommendations attract users who prefer self-directed investment solutions.
Robo-advisory services, powered by AI and algorithms, provide automated investment advice based on user risk profiles and goals. This business model democratizes access to wealth management services, previously limited to high-net-worth individuals, and contributes to financial inclusion.

Insurtech and Digital Insurance
Insurance technology, or insurtech, is another rapidly growing segment. Startups like Acko, Digit Insurance, and PolicyBazaar leverage technology to simplify insurance buying, claims processing, and policy management.
Business models in insurtech include aggregator models, where platforms compare policies from multiple insurers, and direct-to-consumer models, where startups sell policies directly online. Revenue is generated through commissions, policy premiums, and value-added services such as risk assessment tools and claim assistance.
Digital insurance solutions enhance customer experience by reducing paperwork, enabling instant policy issuance, and streamlining claim settlements. Innovative products, such as microinsurance and usage-based insurance, cater to underserved segments and emerging needs.
Neobanking and Challenger Banks
Neobanks and challenger banks are digital-first entities providing banking services without physical branches. Companies like Open, Niyo, RazorpayX, and Jupiter target SMEs, startups, and millennials by offering business accounts, payroll management, expense tracking, and payment solutions.
These startups follow a subscription-based or transaction fee model, offering free basic accounts and charging for premium features, business tools, or API integrations. By focusing on user experience, automation, and real-time analytics, neobanks reduce operational costs while providing efficient banking services to underserved segments.
Neobanking also fosters financial inclusion by providing digital accounts, credit facilities, and payment solutions to small businesses and individuals previously excluded from traditional banking services.
Key Success Factors and Challenges
The success of Indian fintech startups is driven by several factors:
- Digital Infrastructure: UPI, Aadhaar, and widespread internet access facilitate seamless payments and onboarding.
- Regulatory Support: RBI, SEBI, and IRDAI regulations provide frameworks for innovation while ensuring consumer protection.
- Consumer Behavior: Increased smartphone adoption and comfort with digital services accelerate fintech adoption.
- Data Analytics and AI: Leveraging data for credit scoring, personalized services, and fraud detection enhances efficiency and reliability.
However, challenges persist. Regulatory compliance, cybersecurity risks, competition, and customer trust are critical concerns. Startups must navigate complex financial regulations, protect sensitive data, and continuously innovate to maintain competitive advantage.
Future Outlook
The Indian fintech sector is expected to continue its robust growth trajectory, driven by innovation, government support, and increasing financial inclusion. Emerging trends include blockchain-based solutions, cross-border payments, embedded finance, and AI-driven financial advisory services.
Collaborations between fintech startups, traditional banks, and technology providers will further expand service offerings and market reach. Financial literacy programs, targeted solutions for rural and underserved populations, and seamless integration with e-commerce and social platforms will drive adoption in the coming years.
India’s fintech ecosystem is evolving into a mature, diverse, and globally competitive sector, offering scalable business models, innovative solutions, and significant value for consumers, businesses, and investors alike.
Conclusion
Indian fintech startups have transformed financial services by introducing innovative business models in digital payments, lending, wealth management, insurtech, and neobanking. By leveraging technology, data analytics, and digital infrastructure, these startups provide faster, more accessible, and user-friendly financial solutions. While challenges remain, regulatory support, technological innovation, and increasing financial literacy ensure that fintech continues to drive financial inclusion, economic growth, and a robust digital economy in India.
FAQs
1. What are the main business models of Indian fintech startups?
They include digital payments and wallets, lending platforms, wealth management, insurtech, and neobanking services.
2. How do fintech lending platforms work?
They provide digital loans using alternative credit scoring, automated approvals, and faster disbursal compared to traditional banks.
3. What role does technology play in fintech success?
Technology enables seamless transactions, personalized financial services, fraud detection, and data-driven decision-making.
4. What is the future of fintech in India?
Fintech is expected to grow with trends like blockchain solutions, cross-border payments, embedded finance, and AI-driven advisory services.
Next Topic: Ayushman Bharat Scheme: Impact on Healthcare Business
Also Check: Government Infrastructure Projects Shaping India’s Future