The fintech sector in India has emerged as one of the fastest-growing and most dynamic segments of the economy, transforming financial services through technology-driven innovation. From digital payments and lending platforms to wealth management, insurance technology (InsurTech), and blockchain applications, fintech companies are redefining how individuals and businesses access and manage money. This growth has been fueled significantly by venture capital (VC) funding, which provides the financial resources, strategic guidance, and global expertise necessary for scaling innovative solutions in a competitive market.
Understanding venture capital trends in Indian fintech requires examining the sector’s evolution, investment patterns, key drivers, leading investors, challenges, and future prospects. With India’s large population, increasing smartphone penetration, and a growing demand for digital financial services, fintech has become an attractive destination for venture capitalists seeking high-growth opportunities.

Evolution of Fintech in India
The fintech ecosystem in India has evolved rapidly over the past decade. Early innovations focused on digital payments, mobile wallets, and online banking. However, the sector has since expanded to encompass lending platforms, wealth and investment solutions, InsurTech, regulatory technology (RegTech), neobanks, blockchain applications, and financial inclusion initiatives targeting underserved populations.
Several factors have accelerated fintech adoption in India, including:
- Government Initiatives: Programs like Digital India, Jan Dhan Yojana, and UPI (Unified Payments Interface) have expanded digital financial access.
- Smartphone and Internet Penetration: Affordable smartphones and widespread mobile internet have enabled fintech solutions to reach rural and urban populations alike.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Millennials and Gen Z prefer digital, convenient, and real-time financial services over traditional banking channels.
- Regulatory Support: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) have introduced supportive policies to promote digital payments, fintech innovation, and secure financial practices.
This evolving ecosystem has created fertile ground for venture capital investment, with investors seeking to capitalize on India’s rapidly growing digital economy.
Venture Capital Funding Trends in Indian Fintech
1. Rapid Growth of VC Investments
Venture capital funding in Indian fintech has grown exponentially over the past few years. According to industry reports, fintech startups consistently attract a significant share of total VC investments in India, with billions of dollars deployed annually. Key investment segments include payments and digital wallets, lending and credit platforms, wealth management, InsurTech, neobanking, and blockchain-based solutions.
Digital payments remain a dominant area, driven by platforms such as Paytm, PhonePe, and Razorpay. Lending platforms, including fintech companies providing personal loans, SME financing, and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) solutions, have also seen substantial VC interest due to their high growth potential.
2. Focus on Early-Stage and Growth-Stage Funding
VC investors in Indian fintech deploy capital across multiple stages of startup growth. Early-stage funding (seed and Series A rounds) supports product development, market validation, and initial scaling. Growth-stage funding (Series B, C, and beyond) helps startups expand operations, enter new markets, and acquire customers at scale.
Over the past decade, many Indian fintech startups have successfully transitioned from early-stage ventures to unicorn status, reflecting robust investor confidence. Examples include Paytm, Razorpay, CRED, Zerodha, and Pine Labs, which have received multiple rounds of VC funding and have become market leaders.
3. Rise of Neobanks and Digital Lending Platforms
Neobanks, which offer banking services entirely online without physical branches, have emerged as a key area for VC investment. These platforms cater to tech-savvy consumers and SMEs, providing features such as instant account opening, automated bookkeeping, and expense management.
Digital lending platforms, particularly those leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics for credit scoring, have also attracted significant VC capital. Investors are keen to support fintech startups addressing financial inclusion and providing access to credit for underserved populations, including small businesses and rural customers.
4. International Investors and Cross-Border Funding
India’s fintech ecosystem has attracted global venture capital firms, sovereign wealth funds, and strategic corporate investors. International investors bring not only capital but also expertise in scaling fintech solutions, global regulatory insights, and strategic partnerships. Countries such as the United States, Singapore, and the United Kingdom have emerged as key sources of cross-border fintech investment in India.
Leading VC firms actively investing in Indian fintech include Sequoia Capital India, Tiger Global, Accel Partners, Matrix Partners India, and Ribbit Capital. These investors have played a crucial role in nurturing early-stage startups and accelerating the growth of established players.
5. Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory developments in India have significantly influenced venture capital trends in fintech. The introduction of UPI, real-time payments, digital KYC processes, and sandbox frameworks for innovative financial products has increased investor confidence.
However, regulations related to data privacy, digital lending, and consumer protection also present challenges. Startups must comply with RBI guidelines for lending practices, credit scoring, and digital payments while ensuring cybersecurity and data protection. Regulatory clarity and adherence are crucial for attracting and sustaining VC funding.
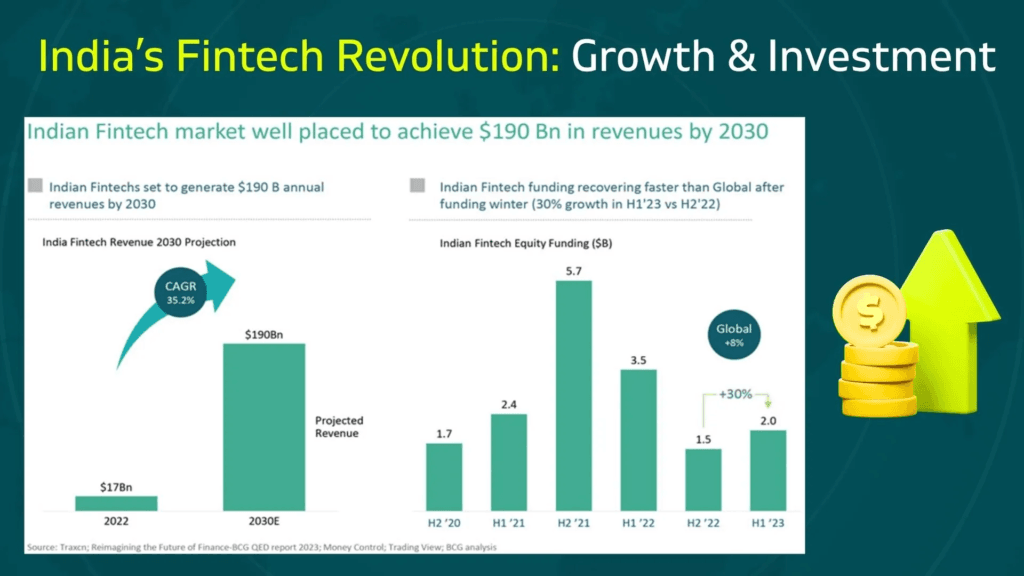
Key Drivers of VC Investment in Indian Fintech
Several factors make Indian fintech an attractive destination for venture capital investment:
- Large Addressable Market: India’s population of over 1.4 billion, combined with increasing smartphone penetration and internet access, creates a massive market for digital financial services.
- Financial Inclusion Initiatives: Government programs promoting banking access and digital payments expand the customer base for fintech solutions.
- Technology Adoption: AI, machine learning, blockchain, and cloud computing enable fintech startups to deliver innovative, scalable, and cost-effective solutions.
- High Growth Potential: Fintech adoption in India is still growing, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, providing room for substantial expansion.
- Investor Confidence: Success stories of unicorns and profitable exits have attracted both domestic and international venture capital firms to fund promising startups.
Challenges Facing Fintech Startups and Investors
Despite the growth opportunities, fintech startups and investors in India face several challenges:
1. Regulatory Uncertainty
Rapid changes in digital lending regulations, KYC norms, and data privacy requirements can affect business operations and investment decisions. Startups must stay compliant while adapting to evolving guidelines.
2. Intense Competition
The fintech sector is highly competitive, with numerous startups competing for market share in payments, lending, neobanking, and wealth management. Differentiating services, acquiring customers, and achieving profitability are ongoing challenges.
3. Credit and Default Risks
Digital lending platforms face risks related to non-performing assets (NPAs) and borrower defaults. Investors must carefully assess credit models, risk mitigation strategies, and recovery processes before funding lending startups.
4. Cybersecurity and Fraud
With increasing digital transactions, cybersecurity threats, fraud, and data breaches are major concerns. Startups must invest in secure systems, compliance frameworks, and consumer protection measures to maintain investor confidence.
5. Scaling Challenges
Scaling fintech solutions across India requires infrastructure investment, customer support, localization of services, and strategic partnerships. Startups must manage operational complexity while maintaining service quality.
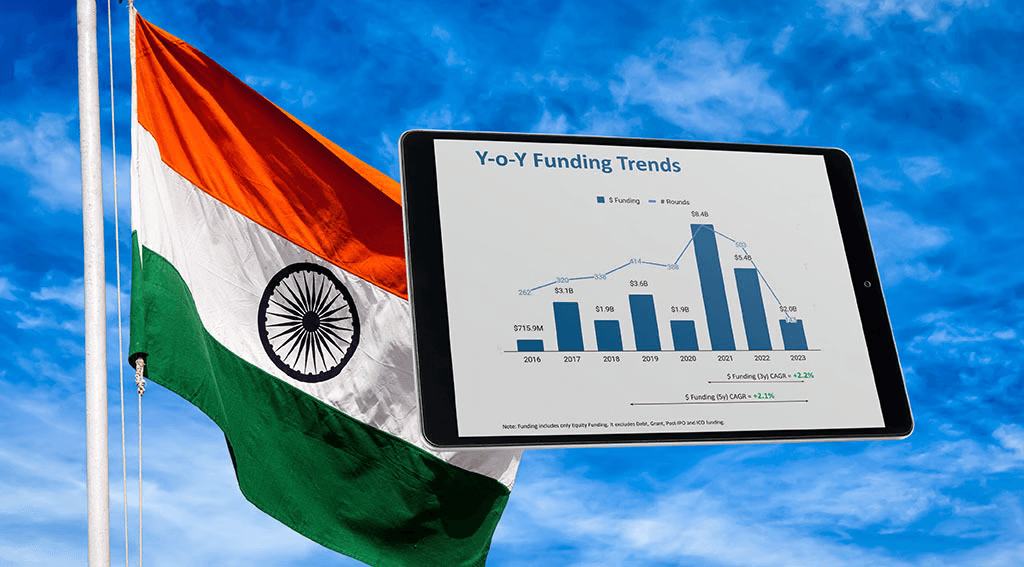
Future Outlook for VC Investment in Indian Fintech
The future of venture capital funding in Indian fintech looks promising due to continued market growth, digital adoption, and government support. Emerging areas likely to attract VC attention include:
- Embedded Finance: Integration of financial services into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce or mobility apps.
- WealthTech and Robo-Advisory: AI-driven investment platforms catering to retail and mass-market investors.
- InsurTech: Digital insurance platforms offering customized products, microinsurance, and streamlined claims processes.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Solutions: Startups exploring secure digital payments, asset tokenization, and decentralized finance (DeFi).
- Financial Inclusion: Platforms targeting underserved populations, small businesses, and rural customers to expand access to credit, savings, and insurance.
With supportive government policies, increasing consumer adoption, and growing investor interest, Indian fintech is expected to remain a high-growth sector, attracting significant venture capital investment over the next decade. Startups that combine innovation, compliance, operational efficiency, and scalability are likely to achieve sustainable growth and create long-term value for investors.
Conclusion / Final Thoughts
Venture capital has been a driving force behind the rapid growth of the Indian fintech sector, enabling startups to innovate, scale, and transform financial services. From digital payments and lending to neobanking, InsurTech, and wealth management, VC funding has provided the capital, strategic guidance, and global expertise necessary to build successful fintech businesses.
Investment trends indicate strong interest from both domestic and international venture capital firms, with funding focused on high-growth areas, early-stage innovation, and scalable business models. Key drivers of VC investment include India’s large and underserved market, technology adoption, government initiatives promoting financial inclusion, and the success of fintech unicorns.
Despite these opportunities, challenges such as regulatory uncertainty, competition, cybersecurity risks, credit defaults, and scaling complexities require careful planning and risk management. Startups that address these challenges while leveraging technology, compliance frameworks, and strategic partnerships are likely to attract sustained VC interest.
As India continues its digital transformation, fintech will play a central role in shaping the future of financial services. Venture capital funding will remain crucial in supporting innovation, expanding access, and driving economic growth in this high-potential sector. The synergy between startups, investors, and policymakers can ensure that Indian fintech continues to thrive, creating value for both consumers and the broader economy.
FAQs
1. Why is venture capital important for Indian fintech startups?
Venture capital provides funding, strategic guidance, global expertise, and risk-sharing necessary for startups to scale, innovate, and compete in the fast-growing fintech sector.
2. Which segments of Indian fintech attract the most VC investment?
Key segments include digital payments, lending platforms, neobanks, InsurTech, wealth management, and blockchain-based solutions.
3. What challenges do VC investors face in Indian fintech?
Challenges include regulatory uncertainty, intense competition, cybersecurity risks, credit and default risks, and operational scaling complexities.
4. What is the future outlook for VC funding in Indian fintech?
The future is promising, with growth expected in embedded finance, InsurTech, wealth management, blockchain solutions, and platforms promoting financial inclusion.
Next Topic: Telemedicine in India: Market Size and Challenges
Also Check: Role of Private Investment in Indian Infrastructure
