Telemedicine, the delivery of healthcare services remotely through digital platforms, has emerged as a transformative force in India’s healthcare sector. By leveraging technology, telemedicine enables patients to consult doctors, access medical advice, receive prescriptions, and even monitor health conditions without visiting healthcare facilities physically. This approach is particularly valuable in a country like India, where healthcare infrastructure is unevenly distributed, and access to quality medical care is often limited in rural and semi-urban areas.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, as lockdowns and social distancing measures made in-person consultations challenging. Today, telemedicine in India encompasses a wide range of services, including virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, digital prescriptions, mental health counseling, chronic disease management, and mobile health applications. The sector has attracted interest from investors, technology companies, and healthcare providers, making it a vital component of India’s digital health ecosystem.
Understanding telemedicine in India requires examining its market size, growth drivers, challenges, regulatory environment, and future potential. While the opportunities are immense, realizing the full potential of telemedicine involves addressing technical, regulatory, infrastructural, and adoption-related hurdles.
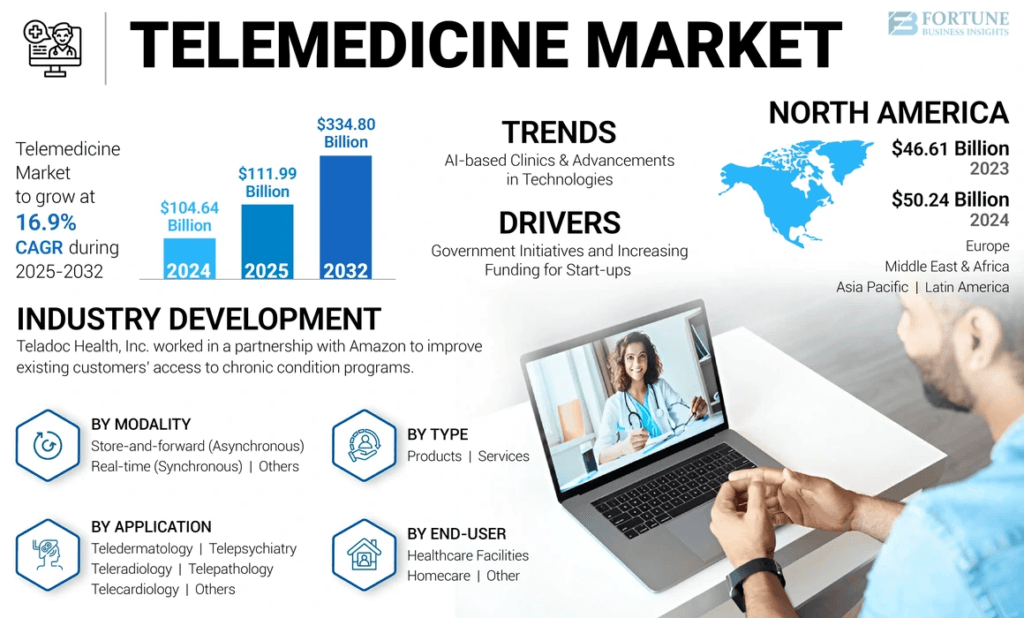
Growth and Market Size of Telemedicine in India
India’s telemedicine market has grown significantly over the past few years, fueled by technological advancements, increased internet penetration, and a shift in patient behavior toward digital healthcare solutions. According to industry reports, the telemedicine market in India was valued at approximately USD 1.3 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 25% in the coming years. Some estimates suggest that the market could exceed USD 5 billion by the late 2020s.
Several factors have contributed to this rapid growth:
- Rural Healthcare Access: Telemedicine bridges the gap between urban medical centers and rural populations, providing remote consultations and reducing travel time and costs.
- Smartphone and Internet Adoption: Affordable smartphones and expanding mobile internet coverage have made telemedicine accessible to a large segment of the population.
- Rise of Chronic Diseases: Increasing prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases has driven demand for remote monitoring and follow-up consultations.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: The pandemic accelerated digital healthcare adoption, highlighting the need for virtual consultations and home-based care.
Key players in India’s telemedicine ecosystem include Practo, 1mg, mfine, DocsApp, Lybrate, and Apollo TeleHealth. Hospitals and healthcare chains, such as Fortis and Apollo Hospitals, have also integrated telemedicine services to expand patient outreach.
Services Offered Through Telemedicine
Telemedicine in India encompasses multiple types of services, enabling healthcare delivery across a wide spectrum:
1. Virtual Consultations
Virtual consultations allow patients to interact with doctors and specialists via video calls, phone calls, or chat-based platforms. These consultations are particularly useful for non-emergency cases, routine follow-ups, second opinions, and mental health counseling.
2. Remote Diagnostics and Monitoring
Telemedicine enables remote diagnostics using connected medical devices, wearables, and mobile health apps. Patients can monitor vital signs such as blood pressure, glucose levels, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, sharing real-time data with healthcare providers for timely interventions.
3. Digital Prescriptions and E-Pharmacy Integration
Doctors can issue digital prescriptions, which patients can use to order medicines online through integrated e-pharmacy platforms. This reduces the need for physical visits, ensures medication adherence, and supports chronic disease management.
4. Tele-ICU and Specialist Services
Advanced telemedicine setups allow remote monitoring of intensive care units (ICUs) and access to specialists in critical cases. This is particularly valuable in smaller hospitals or rural health centers that may lack specialist doctors.
5. Health Education and Preventive Care
Telemedicine platforms provide health education, preventive care tips, and wellness programs to improve patient awareness and encourage proactive healthcare management.
Drivers of Telemedicine Adoption in India
Several factors drive the adoption of telemedicine in India:
- Healthcare Infrastructure Gaps: India faces a shortage of doctors and hospital beds, particularly in rural areas. Telemedicine addresses this imbalance by providing remote access to qualified medical professionals.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Telemedicine saves time and travel costs for patients, making healthcare more accessible and convenient.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Virtual consultations reduce the cost of care delivery, benefiting both healthcare providers and patients.
- Technological Advancements: Mobile apps, AI-based diagnostics, wearable devices, and cloud-based platforms enhance the quality, accuracy, and efficiency of telemedicine services.
- Policy and Regulatory Support: The Indian government’s Telemedicine Practice Guidelines (2020) provide a legal framework for teleconsultations, digital prescriptions, and remote care, fostering investor and consumer confidence.

Challenges in Telemedicine Adoption
Despite its rapid growth and potential, telemedicine in India faces several challenges that limit its widespread adoption:
1. Digital Divide
While smartphone and internet penetration has increased, a significant portion of India’s population, particularly in rural areas, still lacks access to reliable internet connectivity and digital literacy. This limits the reach of telemedicine services and excludes vulnerable populations.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Telemedicine platforms must adhere to guidelines related to patient privacy, data security, digital prescriptions, and medical liability. Ensuring compliance with the Telemedicine Practice Guidelines, IT Act, and Health Data Management regulations can be complex, particularly for startups and smaller providers.
3. Quality and Trust Concerns
Patients often have concerns about the quality of care delivered through virtual consultations. Building trust requires credential verification, standardized protocols, secure platforms, and clear communication to ensure patient safety and satisfaction.
4. Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems
Telemedicine platforms must integrate with hospitals, laboratories, pharmacies, and insurance providers to provide end-to-end care. Fragmentation in healthcare infrastructure can pose logistical and operational challenges for seamless service delivery.
5. Reimbursement and Insurance Coverage
While some health insurers in India are beginning to cover teleconsultations, reimbursement policies are still evolving. Limited insurance support can affect patient adoption and the financial sustainability of telemedicine providers.
6. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
Telemedicine relies heavily on digital platforms to store and transmit sensitive patient data. Ensuring data privacy, protecting against cyberattacks, and complying with regulations such as the Data Protection Act are critical for sustaining patient trust and regulatory compliance.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
To maximize the impact of telemedicine in India, several strategies can be implemented:
- Expanding Internet and Mobile Access: Government initiatives and private partnerships can improve broadband and smartphone penetration in underserved areas.
- Awareness and Education: Training programs and campaigns can increase digital literacy and inform patients about the benefits and safe use of telemedicine.
- Integration with Traditional Healthcare: Collaboration between telemedicine platforms, hospitals, labs, and pharmacies ensures seamless care delivery and better patient outcomes.
- Strengthening Regulatory Frameworks: Clear guidelines on licensing, digital prescriptions, liability, and reimbursement build trust and provide a stable environment for providers and investors.
- Investment in Secure Technology: Telemedicine providers must adopt secure platforms, encryption, and compliance tools to protect patient data and reduce cybersecurity risks.
- Insurance and Payment Support: Expanding insurance coverage and digital payment integration can increase affordability and accessibility for patients.
Future Outlook of Telemedicine in India
The future of telemedicine in India is promising, driven by continued digital adoption, healthcare needs, and government support. Key trends likely to shape the sector include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI-powered diagnostics, predictive analytics, and chatbots can enhance patient care, streamline operations, and reduce costs.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearables, IoT devices, and connected health platforms will enable continuous monitoring of chronic conditions, reducing hospital visits and improving outcomes.
- Tele-ICU and Specialist Networks: Remote access to specialist doctors and ICU monitoring can expand advanced healthcare services to underserved regions.
- Health Insurance Integration: Telemedicine integration with insurance providers will make virtual consultations more affordable and widely adopted.
- Global Collaboration and Medical Tourism: Telemedicine can facilitate international consultations, second opinions, and support India’s growing medical tourism industry.
With these trends, telemedicine is expected to play a crucial role in India’s healthcare ecosystem, making quality medical services more accessible, affordable, and efficient. The combination of technology, regulatory support, and private sector participation positions telemedicine as a transformative tool for the country’s healthcare delivery system.
Conclusion / Final Thoughts
Telemedicine in India represents a significant shift in healthcare delivery, addressing long-standing challenges of access, affordability, and convenience. The sector’s growth has been fueled by digital adoption, government initiatives, rising healthcare needs, and innovative business models. By offering virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, digital prescriptions, and health monitoring, telemedicine provides patients with convenient, cost-effective, and timely medical care.
However, the sector faces challenges such as the digital divide, regulatory complexities, cybersecurity risks, trust and quality concerns, and integration with traditional healthcare systems. Addressing these issues through infrastructure development, regulatory clarity, patient education, secure technology, and insurance support is essential for sustainable growth.
The future of telemedicine in India is bright, with opportunities for AI-driven solutions, remote patient monitoring, tele-ICU networks, and global collaboration. As adoption expands across rural and urban areas, telemedicine is poised to become a core component of India’s healthcare ecosystem, improving access, reducing costs, and enhancing overall health outcomes.
FAQs
1. What is the current market size of telemedicine in India?
The telemedicine market in India was valued at approximately USD 1.3 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 25%, potentially exceeding USD 5 billion in the coming years.
2. What are the main challenges facing telemedicine in India?
Challenges include the digital divide, regulatory compliance, cybersecurity risks, integration with traditional healthcare systems, limited insurance coverage, and concerns about quality and trust.
3. Which services are commonly offered through telemedicine in India?
Common services include virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, digital prescriptions, tele-ICU access, specialist consultations, and health education or preventive care programs.
4. What is the future outlook for telemedicine in India?
The future is promising, with growth driven by AI integration, remote patient monitoring, tele-ICU networks, insurance coverage expansion, and global collaboration, making healthcare more accessible and efficient.
Next Topic: Electronics Manufacturing Boom in India Explained
Also Check: Venture Capital Funding Trends in Indian Fintech
